Navigation auf uzh.ch
Navigation auf uzh.ch
Student's benefit:
Personalized: it goes after the need of every student, not the class as a whole
Mastery-Based: students move on and receive credit only after they mastered a core-concept.
Teaching enrichment:
Teaching and learning methods:
Rotation Model
It goes after the need of every student, not the class as a whole.
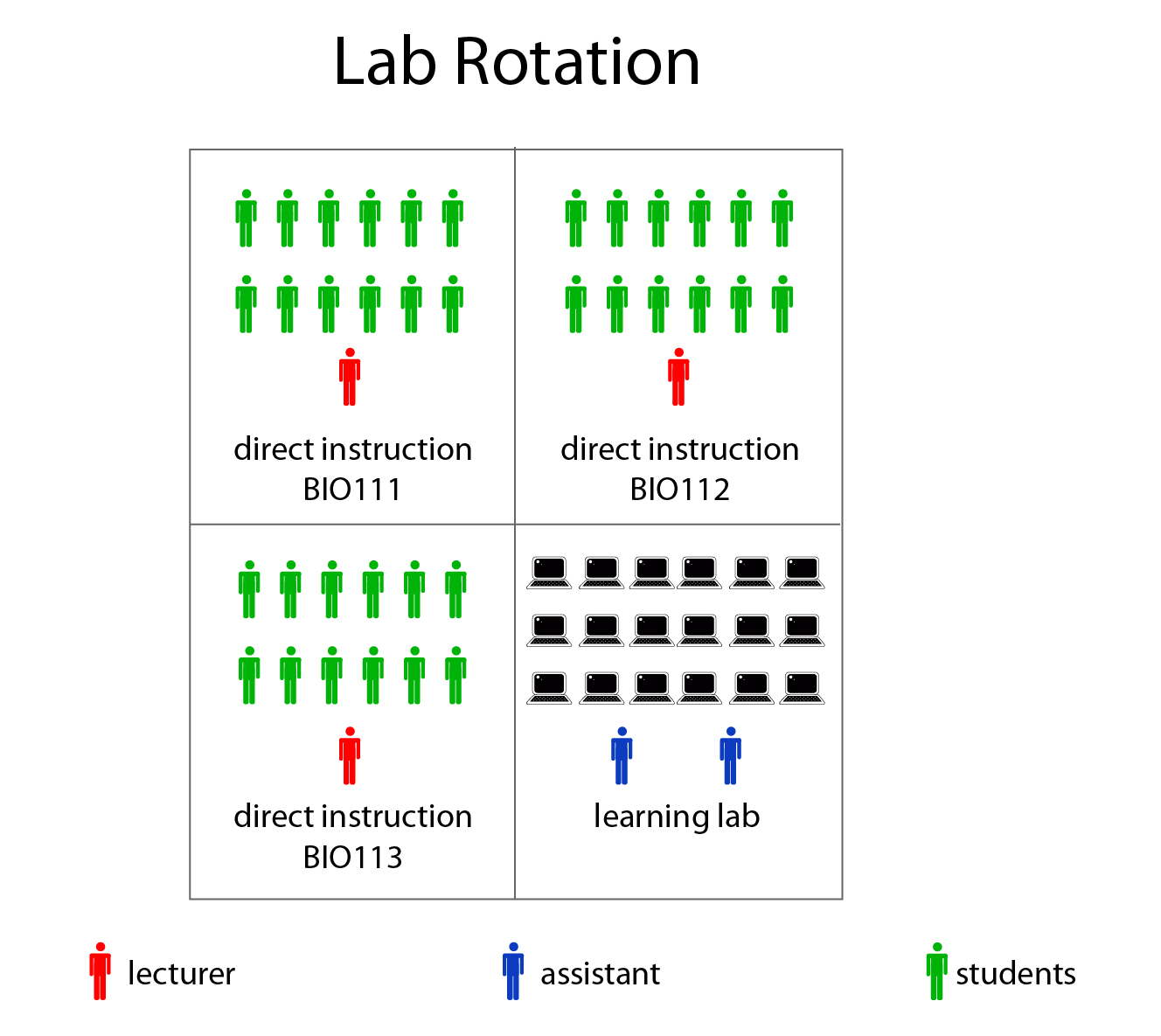
Lab Rotation
Students move on and receive credit only after they mastered a core-concept.
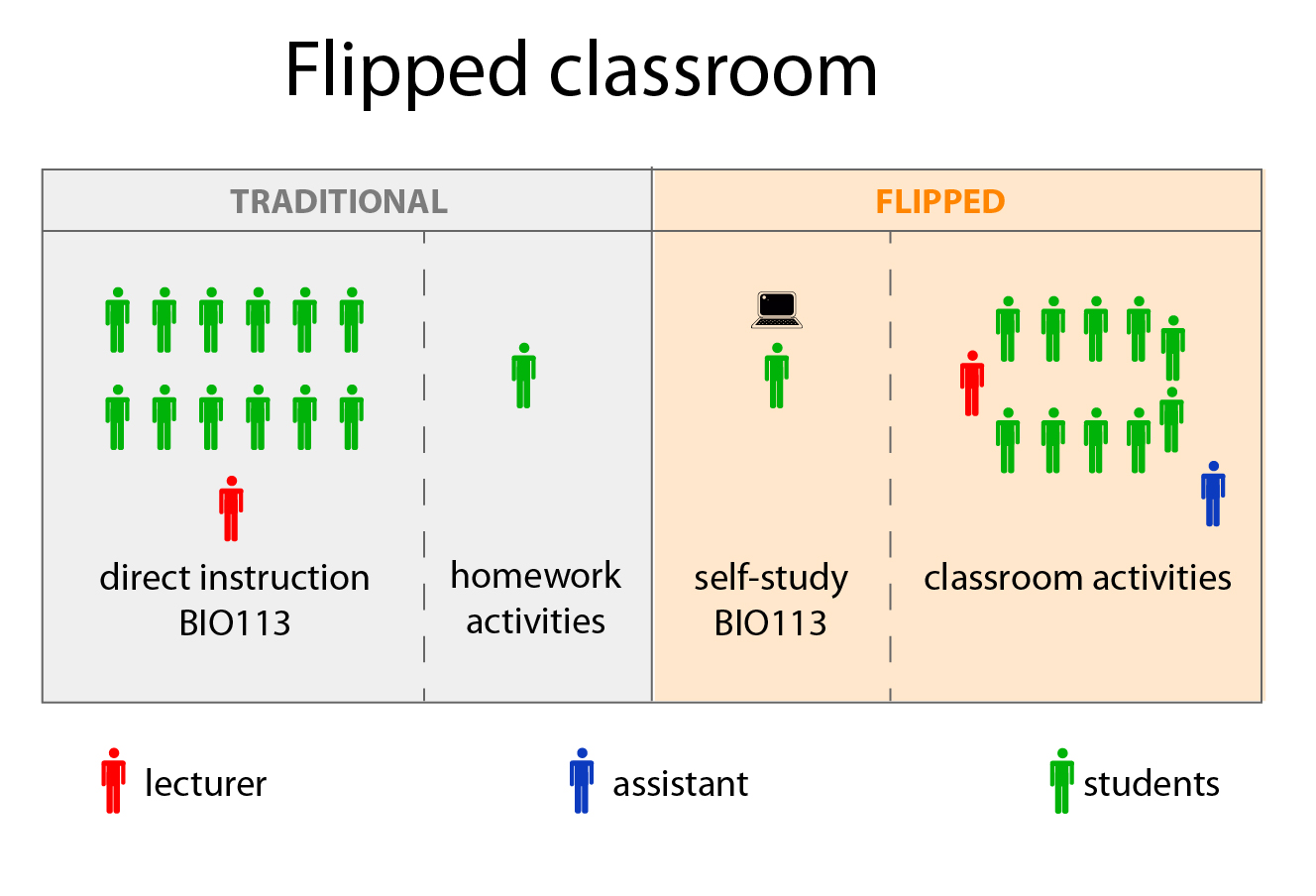
Flipped Classroom
Delivery of instruction online outside of class and moving "homework" into classroom.
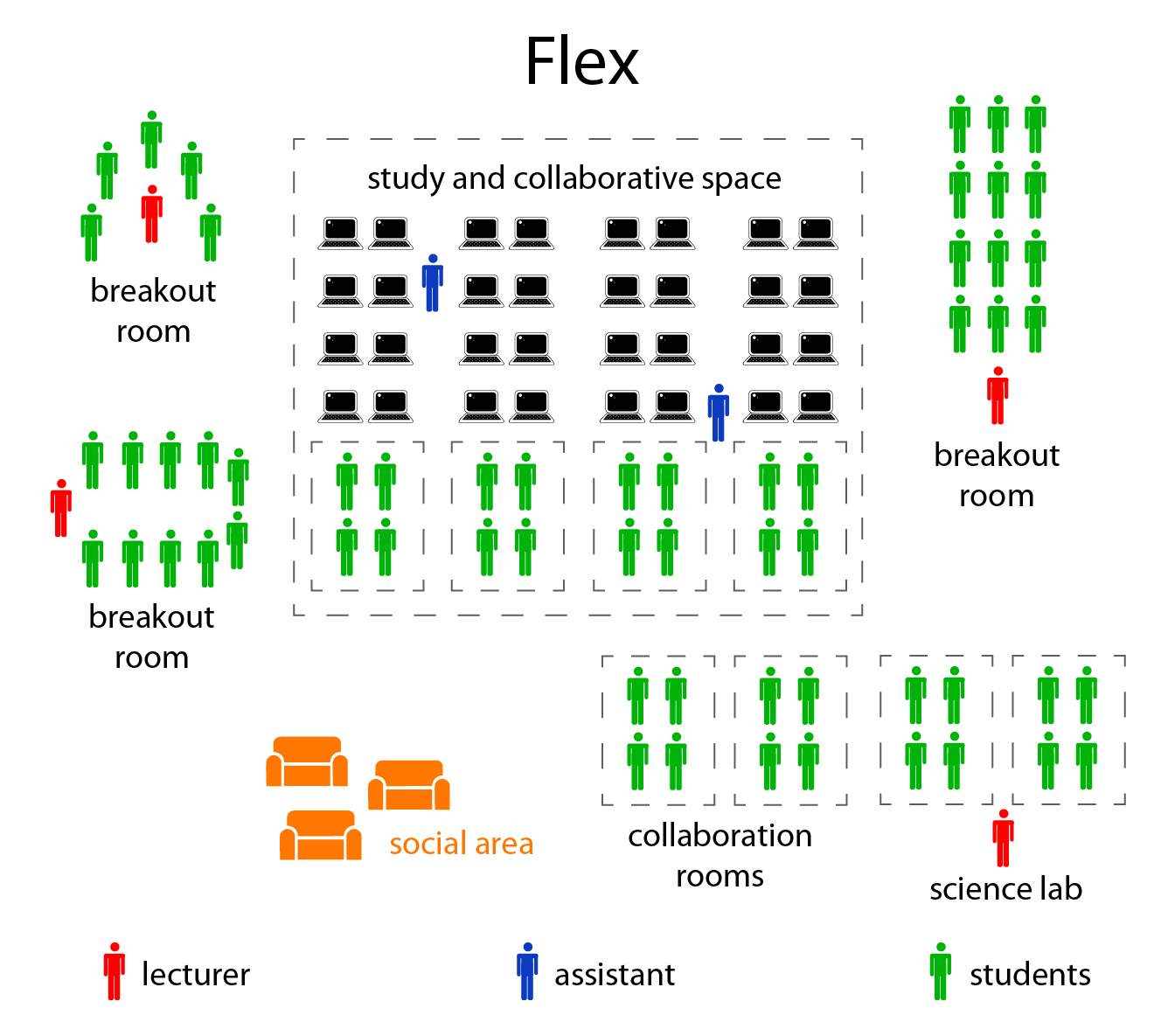
Flex
Students are able to move flexibly through different learning modalities based on their specific needs.
A La Carte model
Students take one or more courses online and at the same time continue to have brick-and-mortar education.
Enriched Virtual model
Students use online delivery of content and instruction next to face-to-face lectures in a certain course.

Blended learning is a formal education program in which a student learns at least in part through online learning, with some element of student control over time, place, path, and/or pace; at least in part in a supervised brick-and-mortar location away from home; and the modalities along each student's learning path within a course or subject are connected to provide an integrated learning experience.
1) Personalized (it goes after the needs of every student, not the class as a whole)
2) Mastery-Based (students move on and receive credit only after they mastered a core-concept)
3) High Expectations (each student has clearly defined rigorous standards)
4) Students Ownership (Student Ownership means that student are empowered with the skills, information and tools that they need to manage their own learning)
The majority of blended-learning programs resemble one of four models: Rotation, Flex, A La Carte, and Enriched Virtual. The Rotation model includes four sub-models: Station Rotation, Lab Rotation, Flipped Classroom, and Individual Rotation. Here are the definitions of these models and sub-models:
A program in which within a given course or subject, students rotate between learning modalities, at least one of which is online learning. Other modalities might include activities such as small-group or full-class instruction, group projects, individual tutoring, and pencil-and-paper assignments.
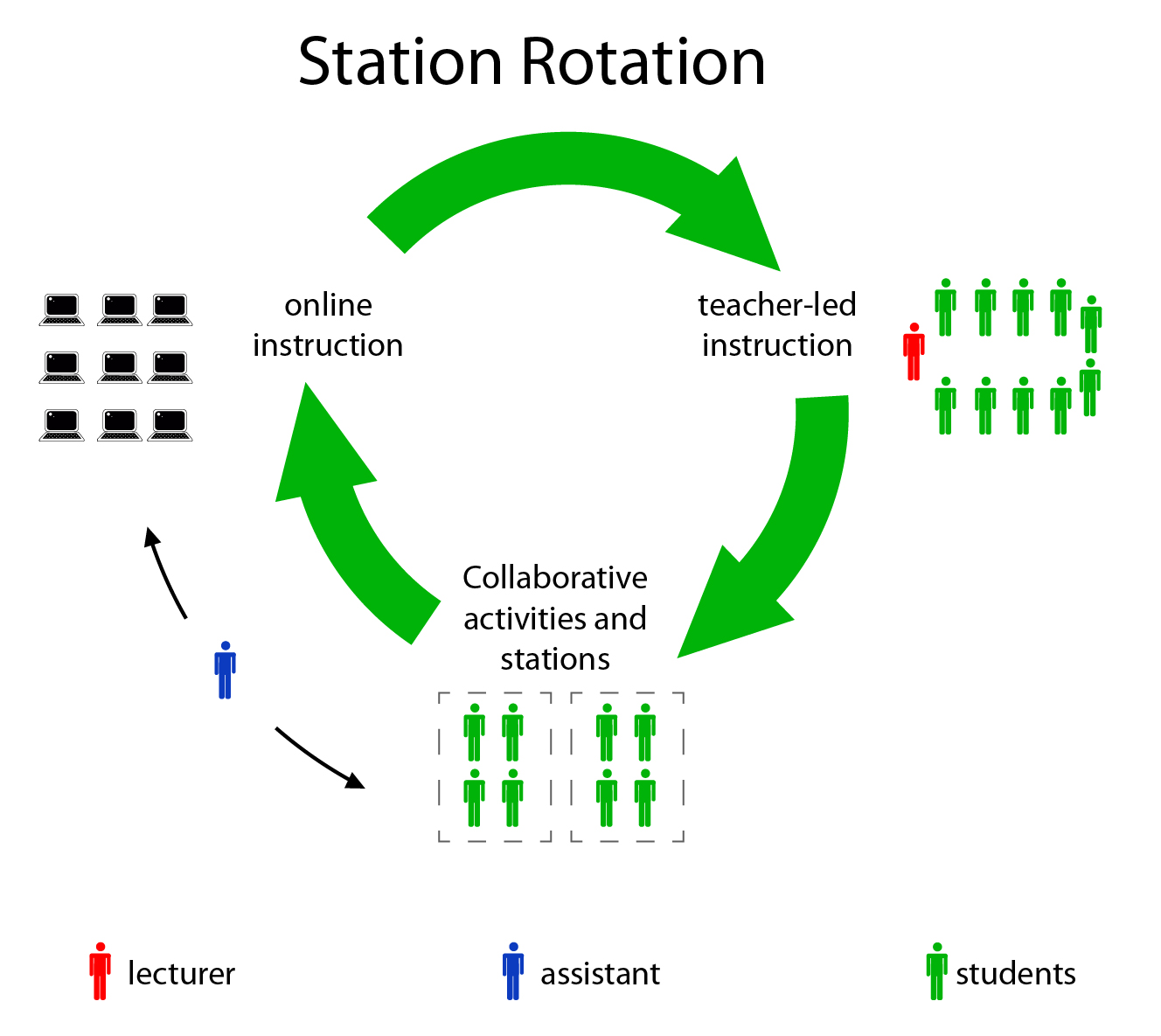
Station Rotation (it goes after the needs of every student, not the class as a whole)
Definition:
Station Rotation (also rferred to as Classroom Rotation or In-Class Rotation) - In a Station within a given course or subject students rotate at fixed points in time - that is, on a fixed schedule or at the teacher's discretion - between different learning stations, at least one of which is an online learning station. Other stations might include activities such as small-group or full-class instruction, group projects, individual tutoring, and pencil-and-paper assignments. Some implementations involve the entire class alternating among activities together, where as other divide the class into small-group rotations. In the Station-Rotation model, students rotate through all of the stations.
(each student has clearly defined rigorous standards)
Definition:
In the Flex model, online learning forms the backbone of a student's learning, even if it directs students to offline activities at times, and students are able to move flexibly through different learning modalities with the goal of optimizing their learning experience based on their specific needs. Each student in essence has a customized, fluid schedule among learning modalities. The teacher of record is on-site, and the teacher-of-record provide face-to-face support on a flexible and adaptive as-needed basis through activities such as small-group instruction, group project, and individual tutoring. Some implementations have substantial face-to-face certified teachers who supplement the online learning on a daily basis, wheras others may provide little face-to-face enrichment and students spend most of their time online; others may have different staffing combinations; describing the staffing model and the amount of time spend online are useful ways to describe different types of Flex models.
Definition:
A program in which students take one or more courses entirely online with an online teacher or record and at the same time continue to have brick-and-mortar educational experiences. Students may take the online courses either on the brick-and-mortar campus or off-site. The differs from full-time online learning and the Enriched Virtual model because it is not a whole-school experinece.
Definition:
A whole-school experience in which within each course, students divide their time between attending a brick-and-mortar campus and learning remotely using online delivery of content and instruction. The Enriched Virtual model differs from the Flipped Classroom because in Enriched Virtual programs, students seldom attend the brick-and-mortar campus every weekday. It differs from the A La Carte model because it is a whole-school experience, not a course-by-course model.